
The Fourth Industrial Revolution
We are in The Fourth Industrial Revolution, 4IR, or Industry 4.0 conceptualizes rapid change to technology, industries, and societal patterns and processes in the 21st century due to increasing interconnectivity and smart automation. Right now, we are going through the Fourth Industrial Revolution, aka Industry 4.0. According to Fortune Business Insights, the global Industry 4.0 market is projected to reach USD 260.71 billion by 2026, a 16.3% CAGR during the forecast period of 2019 to 2026.
Coined popularly by the World Economic Forum Founder and Executive Chairman, Klaus Schwab, it asserts that the changes seen are more than just improvements to efficiency but express a significant shift in industrial capitalism. A part of this phase of industrial change is the joining of technologies like artificial intelligence, gene editing, to advanced robotics that blur the lines between the physical, digital, and biological worlds.
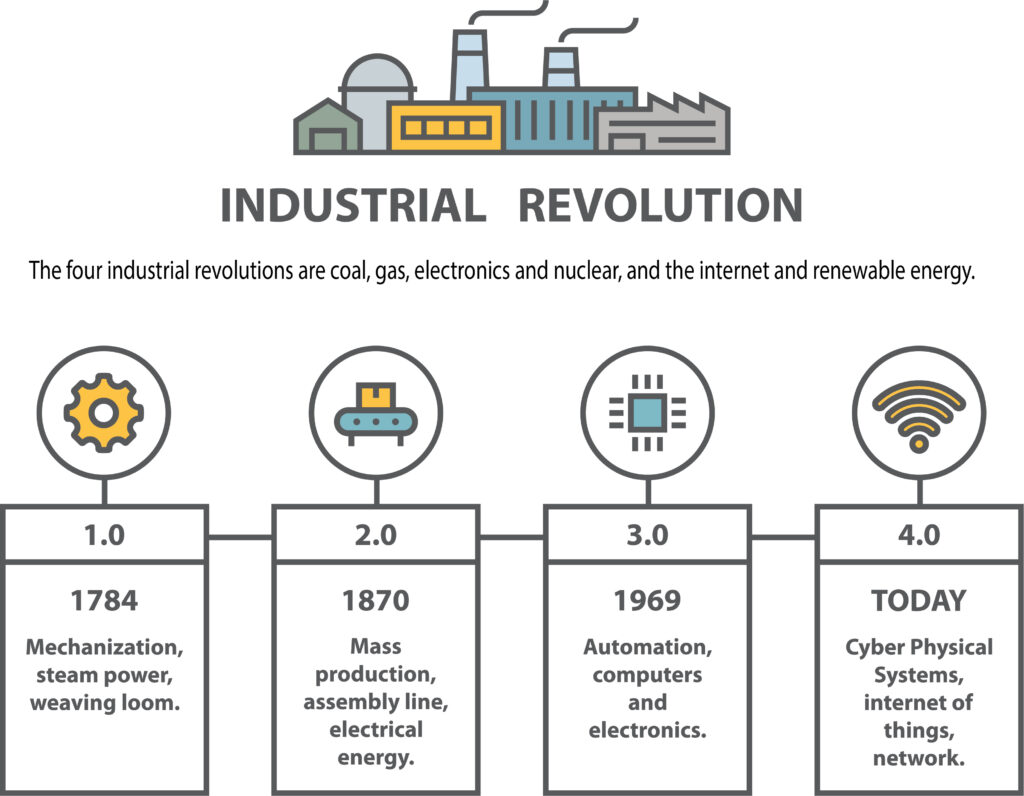
The four industrial revolutions are coal, gas, electronics and nuclear, and the internet and renewable energy. Beginning from 1765 through the present day, we’ve seen an amazing evolution, when steam was harnessed for mechanical production for the first time. The first three industrial revolutions that transformed our modern society. With each of these three advancements—the steam engine, the age of science and mass production, and the rise of digital technology—the world around us fundamentally changed. And right now, it’s happening again, for a fourth time. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, the increasing use of steam power and waterpower, the development of machine tools and the rise of the mechanized factory system

The key drivers of the 4th industrial revolution
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is a way of describing the blurring of boundaries between the physical, digital, and biological worlds. It’s a fusion of advances in artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), 3D printing, genetic engineering, quantum computing, and other technologies.
Technology can not only help business, but also help people be healthier and more productive.
Technology is continually evolving, offering us ever more choices in how we use it to solve business and societal problems. But it can be challenging to keep up: In recent survey of business leaders, 75% of US CEOs said they worried about the speed of technological change. It’s why we should not be focused on continually scanning the tech landscape to understand which innovations will provide the biggest benefits.
Eight emerging technologies and six convergence themes you need to know about.
They include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Augmented Reality (AR)
- Blockchain
- Drones (including driverless vehicles and flying cars)
- Internet Of Things (IoT)
- Robotics
- 3D Printing
- Virtual Reality (VR)
Today, the Essential Eight continue to evolve and make their mark — with the pandemic accelerating emerging tech adoption. Some, like AI, are becoming integral to every type of company. Others, such as 3D printing, have been more concentrated in certain areas like manufacturing. All the while, we’ve been tracking another profound shift: how these individual technologies are combining in transformative ways. While there are other promising technologies like quantum computing and nanotechnology, the most practical and profound impact in the next five years will continue to come from the Essential Eight. But the difference is in how they will work together to deliver this impact.
This convergence reconfigures the eight essential technologies into six power combinations: automating trust, immersive interfaces, extended reality, working autonomy, digital reflection and hyperconnected networks. This wave of innovation promises to significantly expand our capacity to work smarter and more seamlessly with the use of these converged technologies.
Automating trust. What it means
To automate trust, Essential Eight technologies — especially blockchain, IoT and AI — can work together to ensure the authenticity of data, verify identities, and enable secure multiparty transactions. Converged technologies can provide ways to automate trust in physical, digital, and human assets.
How it works
In a typical example, IoT sensors can track a pallet of food from the time it leaves the farm to when it gets to the warehouse and then to the retail store, verifying the entire supply chain. This authenticates where a specific shipment is along the route, as well as the condition of the food during each leg of the journey: Is the shipping container becoming too hot, too cold, or too humid? This information is recorded in a secure, immutable blockchain. Together, IoT and blockchain can create an immutable supply chain, ensuring that buyers are getting an authentic product that has not been damaged or switched along the way. These technologies can also verify whether a product that contains hazardous materials has been disposed of correctly and safely.
Where it’s making an impact
Manufacturers can use automated trust to improve the security of their connected systems and devices, as well as their manufacturing facilities and equipment.
In the healthcare industry, physician networks and hospitals can use trusted tech to confirm each new clinician’s credentials: educational history, licenses, regulatory history and more.
Utilities can use automated trust to confirm numerous contractors in a hurry when they must hire extra crews to respond to a disaster. Any industry can take advantage of tech-enabled corporate reporting to automate trust and improve transparency with investors, regulators and customers while reducing the potential for risk.
Why it matters
Trust is at the heart of all business and personal relationships. If employees, customers, investors, and communities can’t trust the safety, security and privacy of data, systems and processes, your business will suffer. Without trust and transparency, you also could be subject to regulatory and legal actions.
When we look at What are the 6 categories of emerging technologies, and they are and will all be affected. Anything that can be digitized will be digitized. There are 6 categories of technology.
- Construction
- Transportation
- Energy/Power
- Communication
- Manufacturing
- Bio-Related
What does this mean for Fab Lab Armenia Education Foundation?
As an agile and innovative country, you have vase untapped opportunities to grow and lead your country.
Source: Wikipedia. PWC. MIT Media Lab, MIT Technology. Fab Academy



